Google Ends 100 Results per Page: What It Means for Your SEO Metrics
If your SEO reports, Search Console dashboards, or rank-tracking tools are suddenly showing strange drops or weird spikes, you’re not imagining things. Google quietly flipped a change in mid-September 2025 that’s already causing ripple effects across analytics platforms.
It has to do with a setting you may never have noticed: the ability to request 100 organic search results in one page. That’s gone now. 👋🏻
In this post, I’ll walk you through what changed, why it matters (especially for small businesses like yours), and what you can do to adapt without losing your mind.
Table of Contents Show
What Changed (and When)
The old trick: &num=100
For many years, SEO professionals, rank trackers, and power users could append &num=100 to a Google search URL to see up to 100 organic results in one page (instead of the default ~10). This was convenient because one query pulled more data.
In essence:
Before: 1 query → up to 100 results
After: that no longer works
Now: Google returns just ~10 results per page, ignoring or overriding the &num=100 request
In fact, according to Search Engine Land, Google confirmed that the parameter “is not something they formally support.
The timing seems to cluster around September 10–12, 2025. That’s when many dashboards started behaving erratically. It was also right in the middle of a long Google spam update.
Why It’s a Big Deal (Especially for Small Businesses)
You might be thinking, “So what if one search change? I just care about leads.” But this change shakes part of the foundation under many SEO tools and metrics. Here’s why it matters:
1. Rank-tracking and SERP tools had to rework their infrastructure
Because the &num=100 method is gone, tools that used to pull 100 results with a single request now must fetch 10 separate pages (each ~10 results) to reach the same depth. That means:
10× more queries for the same coverage (for example, if you want to see your keyword’s ranking up to position 100)
Higher server load, more bandwidth, more API cost
Some tools temporarily reduced coverage (e.g. only top 20) or updated how often they refresh deeper rankings
Some dashboards broke or showed missing data while their providers scrambled to adjust
So if your rank tool suddenly says “>20” or “not tracked,” that might be why.
2. Reported impressions drop, average position shifts
Another effect: many site owners have already seen a drop in impressions in Google Search Console. Why? Because part of what was being reported before may have come from bot-traffic or from queries using num=100 that are now invalid.
Simultaneously, your average position may look “better” (lower number) because the many very-low-rank placements (pages 3, 4, etc.) may no longer contribute equally to the mix. Basically, some of the “noise” in your ranking metrics is being filtered out.
Important caveat: the actual clicks, traffic, and conversions (what matters to your business) haven’t shifted just because of this change. What has shifted is how Google and tools report your visibility metrics.
3. Less visibility into deeper keyword positions
If a keyword used to rank on page 5 or 8 (which doesn’t get many clicks), tracking it was “nice to know” data. Now, visibility into those deeper positions is harder and costlier. Many tools will limit how far down the ranking chain they go, or only refresh that data less often.
So keywords that were “almost there” may disappear from your reports entirely unless you prioritize them more.
What This Means Long-Term (for Your Analytics and Strategy)
Let me walk you through what this Google tweak suggests about where SEO and analytics are heading, and what small businesses should lean into or pivot away from.
A shift from vanity visibility to business-impact metrics
With impressions and average position becoming less stable (due to reporting inflections), those are less reliable as “success metrics” by themselves. What really matters is:
Clicks
Conversion rate
Leads, sales, revenue
Engagements (if relevant to your business model)
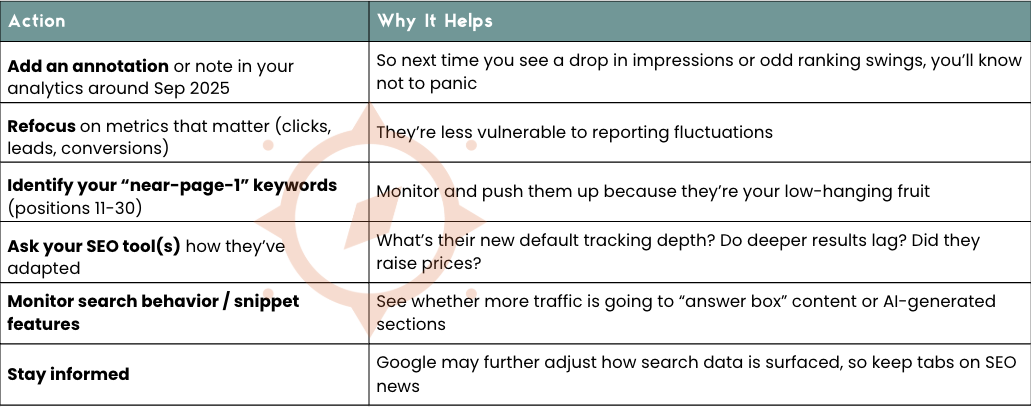
In other words, lean more on action metrics than on big lists of keyword stabs or position tables.
Prioritize your top 10–20 positions
Because deeper positions are harder to monitor and less likely to generate traffic, your SEO effort should increasingly focus on:
Pushing more content and optimization into making it on page 1, especially the top 3–5
Improving click-through (title tags, meta descriptions, structured data, featured snippets)
Monitoring “near page 1” keywords carefully (page 2 or 3) but knowing that data may lag or be less precise
Annotate your dashboards
Because this update is a clear “line in the sand,” it’s smart to annotate your dashboards (or campaign tracking spreadsheets) in September 2025, so that future comparisons don’t mistake the metric shifts for “our SEO is failing.” (It’s not — the data simply changed.)
Keep an eye on SEO tool updates & pricing
This change increases the data-collection burden on rank-tracking providers. That could lead to:
Adjusted defaults (less depth)
Slower refresh rates
Price increases or tiered levels for “deep tracking”
More restrictions on free or entry-level plans
Make sure you’re watching how your tools adapt (and budgeting accordingly).
Be ready for evolving search models (AI overviews, featured snippets)
Google is increasingly surfacing AI and shortcut-style answers (overviews, generative responses) that may bypass the traditional “10 blue links” format. If that continues, optimizing for those snippets or structured answer boxes will matter more. What hasn’t changed is how to optimize: simply focus on EEAT.
This removal of &num=100 might be part of a larger push to reduce “bulk scraping” and steer more toward controlled access or proprietary interfaces.
What You Should Do Right Now (Step-by-Step Checklist)
Here’s a quick plan of action you can roll out to continue monitoring your SEO progress:
A Real-World Analogy (to simplify it)
Imagine you used to get a daily delivery of 100 apples (even if many were far-apart ones). Overnight, the delivery stops, and you get just 10 apples every time, unless you place 10 orders. Your wholesale vendor tells you “We no longer support 100-apple orders in one go.” You haven’t lost trees; you’ve just changed logistics.
In this analogy:
The apples = search result data
The 100-apple order = &num=100 query
The vendor’s new policy = Google removing the parameter
Your task = adjust your system (make more orders or focus on fewer apples)
You’re not doomed, you just need a new process.
Questions about your SEO strategy? Let’s talk!